3 React Hooks Your Next Project Needs
How to Fix Broken Audio in Headphones and Speakers in Linux
The US will finally allow adaptive beam headlights on new cars
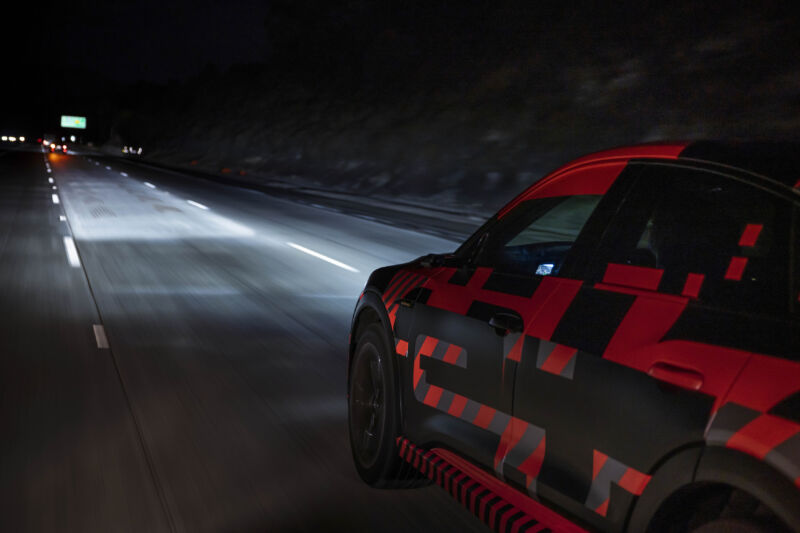

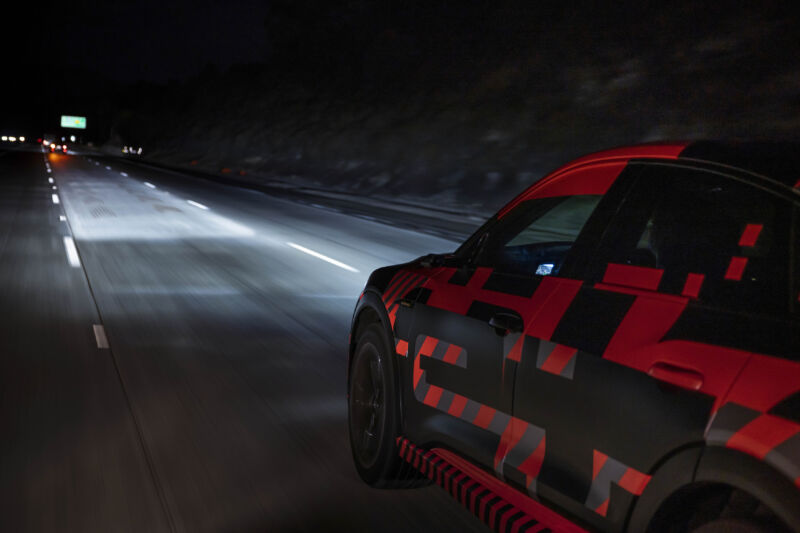
Enlarge / An Audi e-tron prototype on the highway in Europe lights its way ahead with adaptive beam headlights. (credit: Audi)
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is finally poised to legalize adaptive beam headlights in the US. On Tuesday, the NHTSA announced that it has issued a final rule that will update the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, which currently only allow for “dumb” high- and low-beam lights.
Adaptive beam lights use a matrix of projectors, some of which can be turned off to shape the beam so the lights illuminate the road but don’t shine at an oncoming driver. (These are an advancement over the auto-high beam technology that you may have fitted to your current car.) The technology has been around for nearly two decades in Europe and Japan.
Automakers have been asking the NHTSA to update its headlamp rules for some time now. In 2013, Toyota first petitioned the agency to allow for adaptive beam lights, and the NHTSA agreed to begin the laborious and lengthy federal government rulemaking procedure.
How to Audit a Class Online – Learn from Free University Courses
Learn iOS Development by Building a Netflix Clone
Python If-Else – Python Conditional Syntax Example
Google turns old Macs, PCs into Chromebooks with Chrome OS Flex
Whether you have an aging Windows PC in the classroom or a dated Mac in your home office that can’t handle macOS 12 Monterey, Google wants to turn it into a Chromebook. Google today announced early access to Chrome OS Flex, which makes the Chrome OS operating system found on Chromebooks downloadable onto a Mac or Windows PC.
Chrome OS Flex is basically the official Google version of CloudReady, which Google acquired when it bought Neverware in 2020. Flex allows individuals, schools, or businesses to download Chrome OS onto a USB drive for free (CloudReady charges a fee and annual subscription rate to schools and businesses, respectively) and install it onto their Mac or Windows PC. The OS could also be booted from a USB drive instead of installed or launched via network deployment by an IT department.
Google is positioning Chrome OS Flex as an answer to old Mac and Windows PCs that might not be able to handle the latest version of their native OS and/or that might not be owned by folks with budgets to replace the devices. Rather than buying new hardware, consumers or IT departments could install the latest version of Chrome OS Flex.
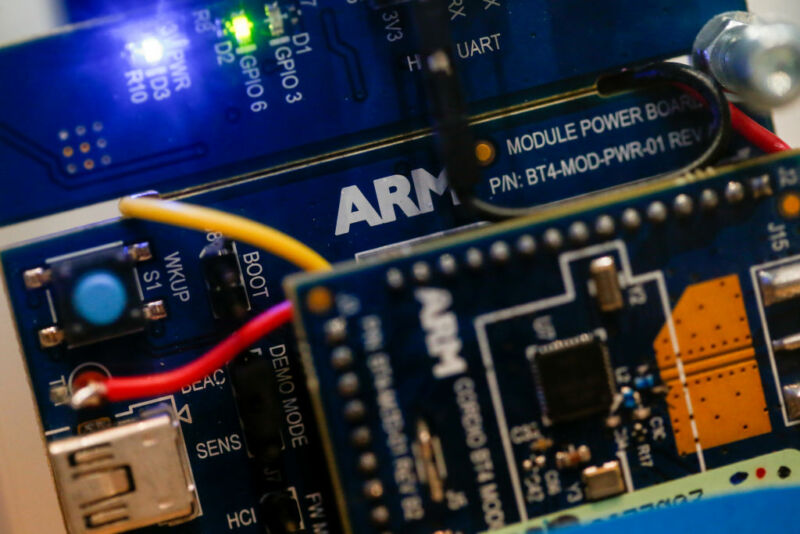
How SoftBank’s costly bet on the “Internet of things” backfired at Arm
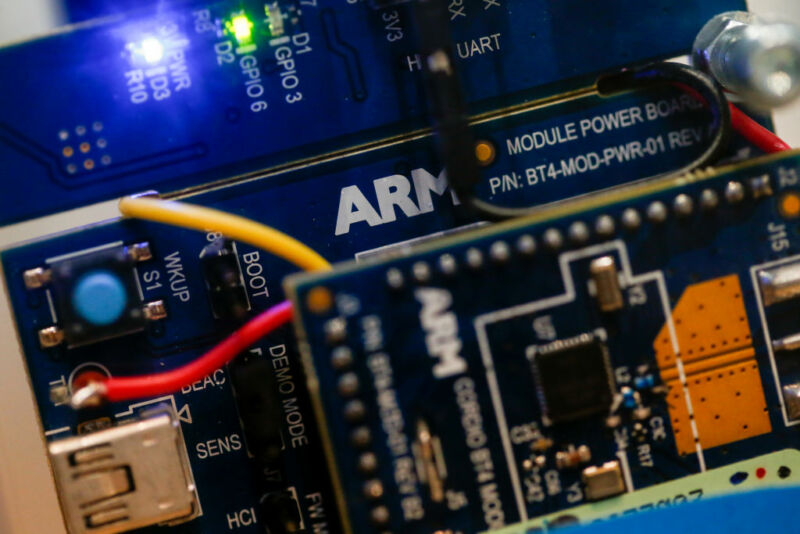
Enlarge / Components manufactured by ARM Holdings Plc sit inside a demonstration ARMmbed parking meter on display on the second day of Mobile World Congress (MWC) in Barcelona, Spain, on Tuesday, Feb. 28, 2017. (credit: Bloomberg | Getty Images)
As Masayoshi Son tried to persuade investors of the wisdom of purchasing one of the most successful chip companies in the world in 2016, the SoftBank chief had one clear message: “For the era of the ‘Internet of things’, I think the champion will be Arm.”
But the concept of connecting billions of everyday and industrial devices to the Internet has been much slower than anticipated to materialize.
Son’s drive to capture the chip design market for the Internet of things (IoT) was the first bet he made on Arm that has not paid off. The second was a $66 billion sale of the company to Nvidia that unraveled last week.