
A case study showing that measuring CSAT is the starting point, but you can also use that data to ensure an improved experience. Read More

A case study showing that measuring CSAT is the starting point, but you can also use that data to ensure an improved experience. Read More

For the cult classic Stargate science fiction franchise,character and plot development was helmed by Stargate co-creator Brad Wright. In 2021, Wright publicly posted a message on Twitter<asking if it was possible for AI to write an episode of Stargate , None other than Laurence Moroney, AI lead at Google, picked up the gauntlet.Read More
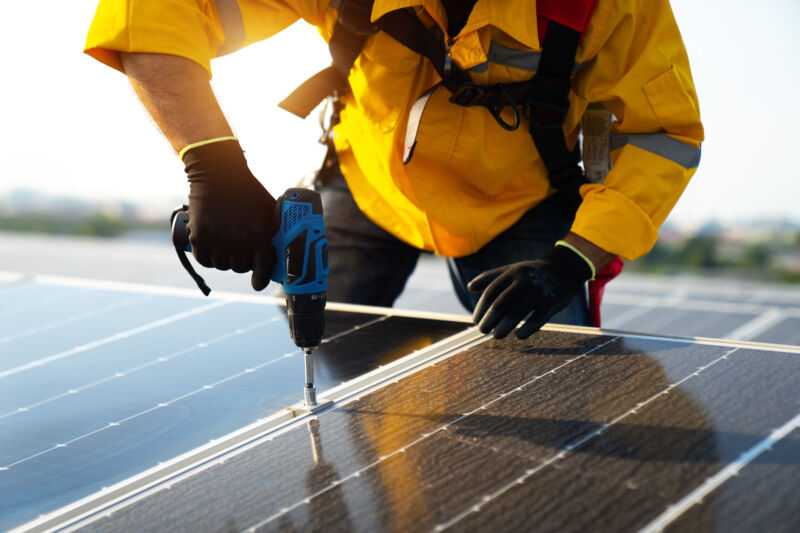

Enlarge / The Electrify America Solar Glow 1 farm will generate enough solar power to offset the entire EA charging network.
One of the best things about electric cars, other than their power trains, immediate torque, and relaxing quiet, is the fact that as the electrical grid becomes cleaner, so too does every EV that uses that grid to charge. That process took a step forward this week with the news that by next year, the Electrify America (EA) charging network will be entirely offset by solar energy.
On Wednesday, EA signed a 15-year agreement with Terra-Gen to purchase electricity from a 75 MW solar farm being built by the latter in San Bernardino County, California. In the past, Tesla CEO Elon Musk has made various promises about making Tesla’s Supercharger network entirely solar-powered, and the automaker has installed solar arrays at some of its charging locations. It does not appear that the network is fully solar-powered yet, though.
The Electrify America Solar Glow 1 project will break ground later this year, and when it’s fully operational in 2023, it should have an annual energy production of 225,000 MWh. That’s more than enough to account for the annual energy use of the EA charging network.
Second Dinner and Nuverse announced Marvel Snap today, a new digital collectible card game that is coming to PC and mobile.Read More
Dr. Sephus discusses breaking down barriers to machine learning at Ars Frontiers 2022. Click here for transcript. (video link)
Welcome to the week after Ars Frontiers! This article is the first in a short series of pieces that will recap each of the day’s talks for the benefit of those who weren’t able to travel to DC for our first conference. We’ll be running one of these every few days for the next couple of weeks, and each one will include an embedded video of the talk (along with a transcript).
For today’s recap, we’re going over our talk with Amazon Web Services tech evangelist Dr. Nashlie Sephus. Our discussion was titled “Breaking Barriers to Machine Learning.”
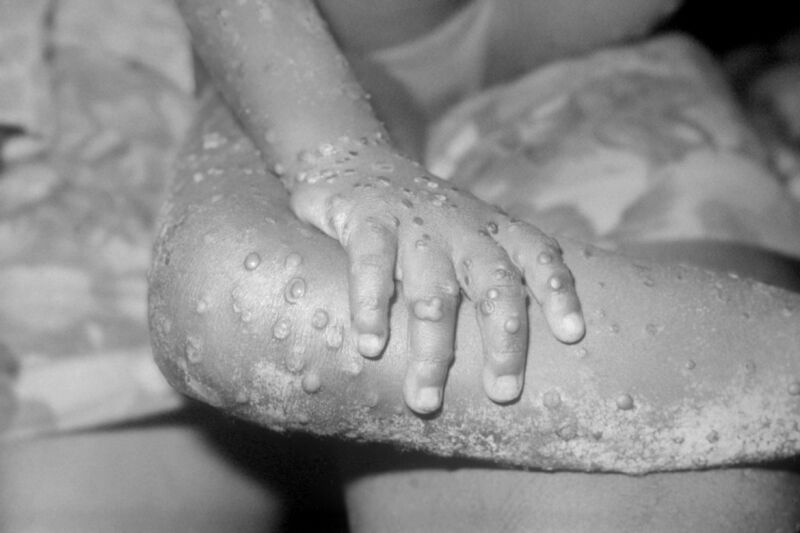
Enlarge / A 2003 photo of the arms and legs of a 4-year-old girl infected with monkeypox in Liberia. (credit: Getty | BSIP)
A growing outbreak of monkeypox cases has spread across several countries, including the US, suggesting that the animal-transmitted disease that occurs in forested areas of Central and West Africa has been quietly spreading undetected.
So far, the US has reported one case in a Massachusetts man who had recently traveled to Canada, which, as of Thursday, reported 17 suspected cases in Montreal. The United Kingdom has identified nine cases, one of which is connected to recent travel to Nigeria, where monkeypox is endemic. But the other cases appear to have been infected within the UK and are all not linked to the travel-related case by contact or timing. Portugal is investigating more than 20 cases, Spain is reportedly investigating 23 cases, and Italy and Sweden have each reported at least one case.
Monkeypox is a relative of smallpox and produces similar symptoms, but it causes a milder disease than that of the eradicated virus. There are two clades of monkeypox: the West African clade and the Congo Basin clade. The West African clade, which is what has been detected in the UK, is the milder of the two. It is usually a self-limiting infection, though it can cause severe disease in some cases. The case fatality rate has been estimated at about 1 percent. The Congo Basin clade, meanwhile, has an estimated fatality rate of as high as 10 percent. For both clades, children are among those at high risk of severe disease, and infection can be particularly dangerous during pregnancy, causing complications, congenital conditions, and stillbirth.
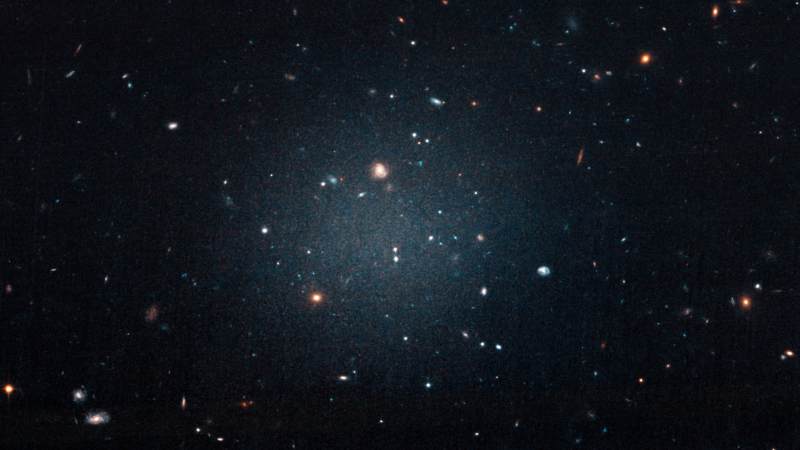

Enlarge / The dark matter-poor galaxies are so diffuse that you can see right through them. (credit: NASA, ESA, and P. van Dokkum)
The Universe’s first galaxies are thought to have formed at sites where a lot of dark matter coalesced, providing the gravitational pull to draw in enough regular matter to create stars. And, to date, it’s impossible to explain the behavior of almost all the galaxies we’ve observed without concluding that they have a significant dark matter component.
Almost, but not all. Recently, a handful of galaxies have been identified that are dim and diffuse, and appear to have relatively little dark matter. For a while, these galaxies couldn’t be explained, raising questions about whether the observations had provided an accurate picture of their composition. However, researchers recently identified one way the galaxies could form: A small galaxy could be swallowed by a larger one that keeps the dark matter and spits out the stars.
Now, a second option has been proposed, based on the behavior of dark matter in a galaxy cluster. This model may explain a series of objects found near the dark matter-poor galaxies. And it may suggest that galaxy-like objects could be formed without an underlying dark matter component.

Ivanti’s Ransomware Index Report Q1 2022, released today, helps to explain why ransomware is becoming more lethal.Read More